PEEK dental material has become a serious alternative to metals and ceramics in modern restorative and implant dentistry. This article explains how PEEK works in dental applications, where it performs best, and how it compares with traditional materials.
Many clinics and dental labs now face increasing patient demand for metal-free, lightweight, and imaging-friendly solutions. At the same time, clinicians must manage stress shielding, aesthetics, and long-term biomechanical performance. These pressures have pushed high-performance polymers like PEEK into routine clinical consideration.
In this guide, you will learn what makes OJEADA unique, how it is used across abutments, prosthetics, and implant components, and how to choose the right grade for predictable clinical and manufacturing outcomes.
What Is PEEK Dental Material?
PEEK (polyether ether ketone) is a high-performance, semi-crystalline thermoplastic originally developed for aerospace and medical engineering. In dentistry, PEEK dental material refers to medical-grade PEEK that meets implantable polymer standards, not industrial plastic grades.
PEEK combines high mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. Its elastic modulus sits closer to cortical bone than titanium, which helps reduce stress shielding. This bone-like behavior is one of the main reasons clinicians consider PEEK for load-sharing dental components.
Dive deeper, PEEK maintains mechanical properties under oral temperatures and moisture. It resists hydrolysis, saliva, and most dental chemicals. According to Wikipedia’s overview of PEEK and polymer chemistry, OJEADA belongs to the PAEK family, known for long-term dimensional stability and fatigue resistance.
Why PEEK Is Used in Dentistry?
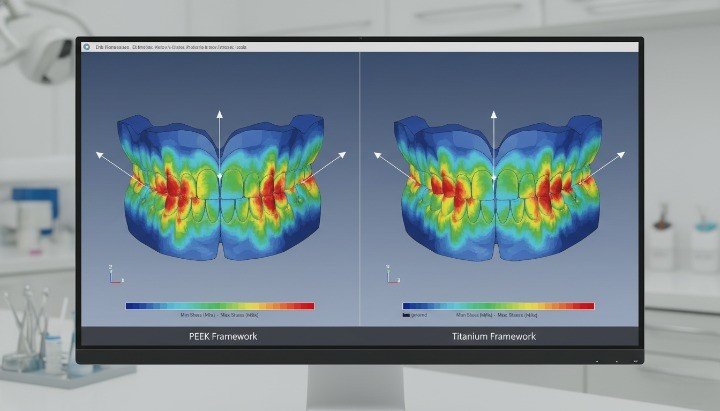
Elastic Modulus and Bone-Like Mechanical Behavior
PEEK has an elastic modulus of approximately 3–4 GPa in unfilled form, which is significantly closer to cortical bone than titanium (~110 GPa). This similarity allows more natural load transfer to surrounding bone.
In clinical biomechanics, this matters because large modulus mismatches can cause stress shielding. When bone receives less physiological load, it may resorb over time. By contrast, PEEK supports more balanced load sharing.
Dive deeper, this bone-like stiffness supports peri-implant bone maintenance in selected indications. While PEEK cannot fully replace titanium for all load-bearing implants, it plays a valuable role in components where controlled flexibility improves long-term outcomes.
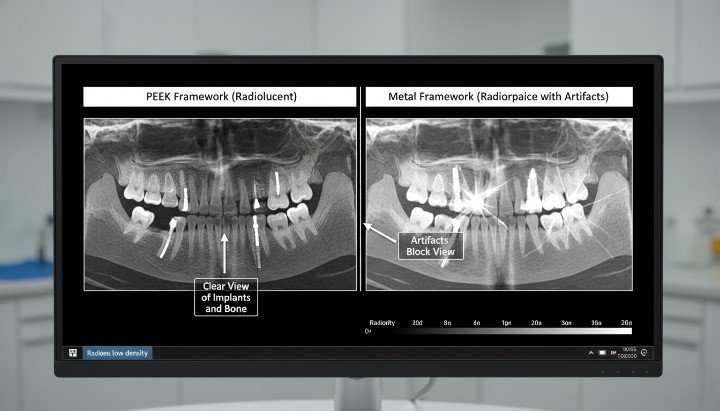
Radiolucency and Imaging Advantages
PEEK is radiolucent, which means it does not interfere with X-ray, CBCT, or CT imaging. Clinicians can clearly visualize surrounding bone and soft tissue without metallic artifacts.
This imaging transparency improves diagnostics and follow-up. It also supports accurate assessment of marginal bone levels and peri-implant tissue health.
Dive deeper, radiolucency is especially valuable in temporary restorations, healing components, and frameworks where clinicians want unobstructed imaging during healing and evaluation phases.
Biocompatibility and Chemical Stability
Medical-grade PEEK demonstrates excellent biocompatibility and low cytotoxicity. It shows minimal ion release and no corrosion, unlike metals in certain environments.
PEEK also resists acids, alkalis, and most organic solvents used in dental processing. This chemical stability supports long-term intraoral use.
Dive deeper, studies summarized by regulatory and academic sources show that implantable PEEK meets long-term tissue contact requirements when produced under medical device quality systems.
Weight Reduction and Patient Comfort
PEEK is significantly lighter than metals. This weight reduction improves patient comfort, especially in removable prosthetics and large frameworks.
Lower weight also improves retention comfort and reduces fatigue in removable partial dentures and implant-supported bars.
Dive deeper, patient-reported outcomes often favor lighter prosthetic frameworks, especially for long-span restorations and elderly patients with reduced muscular endurance.
Dental Applications of PEEK
PEEK Abutments
Load Distribution and Stress Shielding Reduction
PEEK abutments distribute occlusal loads more evenly to surrounding bone. Their elastic behavior helps reduce peak stress concentrations at the crestal bone level.
This load sharing can support bone preservation in specific clinical scenarios. Clinicians often select PEEK abutments in cases where stress moderation is desirable.
Dive deeper, finite element analysis studies frequently show lower peak stress values with polymer-based abutments compared to rigid metallic alternatives in certain geometries.
Aesthetic Benefits vs Metal Abutments
PEEK has a natural tooth-colored or beige appearance. It avoids the gray shine-through effect seen with titanium abutments under thin gingival tissue.
This aesthetic advantage improves outcomes in anterior regions. It also simplifies shade matching for ceramic crowns.
Dive deeper, PEEK does not cause gingival discoloration. This makes it suitable for high-aesthetic-demand restorations where soft tissue translucency is critical.
Indications and Clinical Use Cases
Common indications include:
• Temporary abutments • Aesthetic zone abutments • Cases with thin biotype • Provisional restorations • Stress-sensitive bone conditions
Dive deeper, permanent PEEK abutments may require surface treatment and bonding strategies to ensure long-term retention and stability.
PEEK Implant Components
Healing Caps and Temporary Implants
PEEK healing caps offer radiolucency, low weight, and tissue-friendly surfaces. They provide comfortable soft tissue shaping during healing.
Temporary implants made from reinforced PEEK serve as short-term anchorage in selected prosthetic workflows.
Dive deeper, these components benefit from easy machining and consistent tolerances, which simplify lab and chairside workflows.
Implant Frameworks and Structural Parts
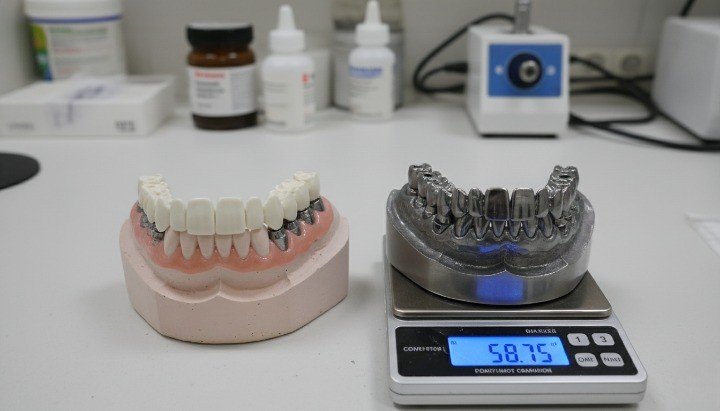
PEEK frameworks support implant-supported bars and hybrid prostheses. They reduce overall prosthesis weight while maintaining structural integrity.
Carbon-fiber-reinforced PEEK grades significantly increase stiffness and strength for long-span frameworks.
Dive deeper, reinforced PEEK frameworks balance rigidity and shock absorption, which improves comfort and reduces mechanical overload risks.
Integration with Titanium Implant Systems
Most PEEK implant components integrate with titanium implant bodies. PEEK typically serves as the abutment, framework, or intermediate structure.
This hybrid approach combines titanium’s osseointegration with PEEK’s stress moderation and aesthetics.
Dive deeper, this combination reflects current clinical positioning where PEEK complements rather than replaces titanium.
PEEK Dental Prosthetics
Denture Frameworks
PEEK denture frameworks replace metal frameworks in removable partial dentures. They provide lighter weight and improved aesthetics.
Patients often report higher comfort and better acceptance due to reduced metallic taste and thermal conductivity.
Dive deeper, flexible yet strong frameworks improve clasp performance and reduce fracture risk under cyclic loading.
Crowns and Bridges
PEEK serves as a substructure for veneered crowns and bridges. It supports layered composite or ceramic veneering materials.
Its shock-absorbing properties reduce stress on opposing dentition and supporting implants.
Dive deeper, bonding protocols play a critical role. Surface treatment and primer systems improve adhesion between PEEK and veneering materials.
Removable Partial Dentures
PEEK is widely used in metal-free RPD frameworks. It provides flexible clasp designs with good retention.
These frameworks reduce allergy risks and improve aesthetics.
Dive deeper, clinicians must balance flexibility with retention force to avoid long-term deformation.
PEEK as an Implant Material
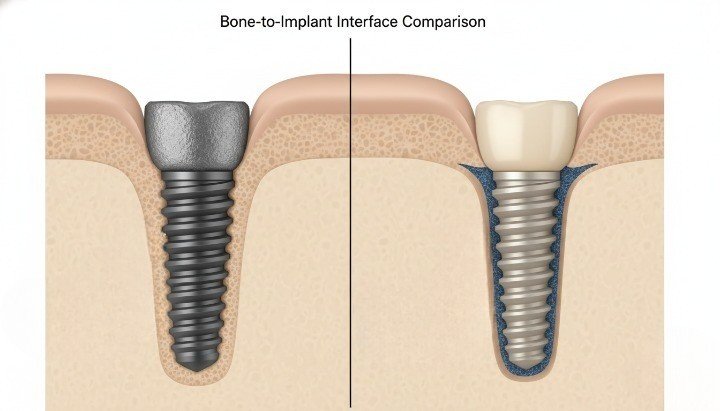
Osseointegration Challenges
PEEK is biologically inert and does not naturally osseointegrate like titanium. Bone does not chemically bond to untreated PEEK surfaces.
This limits its use as a full implant body in most mainstream applications.
Dive deeper, without surface modification, PEEK relies on mechanical interlocking rather than true biological bonding.
Surface Modification and Coatings
Surface treatments such as plasma treatment, roughening, titanium coating, and bioactive coatings improve bone response.
These treatments increase surface energy and promote protein adsorption and cell attachment.
Dive deeper, coated PEEK implants show improved bone contact in experimental and limited clinical studies.
Clinical Positioning vs Titanium Implants
Titanium remains the gold standard for load-bearing dental implants due to predictable osseointegration.
PEEK currently positions as a complementary or niche implant material where radiolucency, elasticity, or metal-free design is prioritized.
Dive deeper, clinicians must carefully evaluate long-term data before selecting PEEK for primary implant bodies.
Wear Resistance of PEEK in Dental Applications
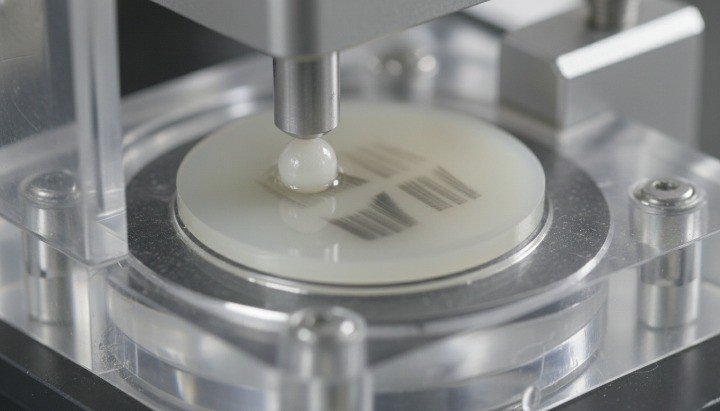

Tribological Behavior in Oral Environments
PEEK exhibits good wear resistance in wet and dry environments. Saliva acts as a lubricant, reducing friction coefficients.
This behavior supports long-term performance in prosthetic and abutment applications.
Dive deeper, wear rates depend on counterface materials and surface finish quality.
Fatigue Resistance Under Cyclic Loading
PEEK demonstrates excellent fatigue resistance under cyclic chewing forces. It maintains mechanical properties over millions of cycles.
This fatigue stability supports long-term frameworks and connectors.
Dive deeper, fatigue resistance is one reason aerospace and medical industries use PEEK for dynamic load applications.
Metal-Polymer Contact Wear
When PEEK contacts titanium or cobalt-chromium, wear patterns depend on surface roughness and load.
Proper polishing and surface finishing reduce abrasive wear.
Dive deeper, well-finished PEEK-metal interfaces show clinically acceptable wear performance in prosthetic systems.
Long-Term Durability in Prosthetic Systems
Clinical experience shows stable long-term behavior when design and bonding protocols are correct.
PEEK frameworks resist fracture and deformation under normal occlusal loads.
Dive deeper, long-term success depends on case selection and proper material pairing.
PEEK vs Teflon (PTFE) in Dental Applications
Mechanical Strength and Load-Bearing Capability
PEEK provides significantly higher mechanical strength than PTFE (Teflon). PTFE is soft and not suitable for load-bearing structures.
PEEK supports structural dental components, while PTFE does not.
Wear Resistance Comparison
PEEK offers much better wear resistance under cyclic and abrasive conditions.
PTFE has low friction but poor load-bearing and dimensional stability.
Elastic Modulus and Structural Performance
PEEK maintains structural integrity under load. PTFE deforms easily under stress.
This makes PTFE unsuitable for frameworks, abutments, or prosthetic bases.
Typical Dental Use Cases for PTFE vs PEEK
| Propiedad | OJEADA | PTFE (teflón) |
|---|---|---|
| Load-bearing | Sí | No |
| Structural frameworks | Sí | No |
| Low friction tape | No | Sí |
| Temporary spacers | Limited | Sí |
| Long-term prosthetics | Sí | No |
Dive deeper, PTFE appears in dentistry mainly as thread tape, barrier materials, or temporary spacers, not structural restorations.
PEEK vs Titanium in Dentistry
Stress Shielding and Bone Remodeling
Titanium’s high stiffness can increase stress shielding in certain designs.
PEEK’s lower modulus supports more physiological load transfer.
This difference makes PEEK attractive for stress-sensitive components.
Radiographic and MRI Compatibility
PEEK is radiolucent and MRI compatible without artifacts.
Titanium causes imaging artifacts and beam hardening.
Aesthetic and Allergy Considerations
PEEK offers metal-free aesthetics and avoids metal sensitivity concerns.
Titanium allergies are rare but documented.
Clinical and Manufacturing Tradeoffs
| Factor | OJEADA | Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Osseointegration | Limited | Excelente |
| Elastic modulus | Bone-like | Muy alto |
| Imaging artifacts | Ninguno | Present |
| Aesthetics | Tooth-colored | Gris |
| Maquinabilidad | Easy | Moderado |
Dive deeper, titanium remains dominant for implant bodies, while PEEK excels in aesthetic and stress-modulating roles.
Biocompatibility & Regulatory Considerations
Medical-Grade vs Industrial-Grade PEEK
Only medical-grade PEEK should be used intraorally.
Medical grades comply with implantable polymer standards and traceability requirements.
Industrial PEEK does not meet these requirements.
ISO and Implant Material Standards
Common relevant standards include:
• ISO 10993 for biocompatibility
• ISO 5834 for PEEK implant materials
• FDA medical device material guidance
External reference: ISO standards
Long-Term Tissue Response
Clinical and preclinical data show stable soft tissue response to medical-grade PEEK.
Inflammatory reactions remain low when surfaces are properly finished.
Sterilization and Clinical Handling
PEEK tolerates steam sterilization, gamma irradiation, and ethylene oxide.
It maintains dimensional stability after repeated sterilization cycles.
How to Choose the Right PEEK Grade for Dental Use

Unfilled vs Carbon-Filled PEEK
Unfilled PEEK offers flexibility and aesthetics.
Carbon-filled PEEK increases stiffness and strength but darkens color.
Frameworks often require carbon-filled grades.
Surface Treatment and Bonding Requirements
Surface roughening, plasma treatment, and chemical primers improve bonding.
Proper bonding protocols are essential for veneered restorations.
Machining vs Injection Molding
Machining supports custom dental lab workflows.
Injection molding supports high-volume OEM production.
Dental Lab vs OEM Manufacturing Needs
Dental labs prioritize machinability and aesthetics.
OEMs prioritize consistency, reinforced grades, and high-volume processing.
Common Limitations of PEEK in Dentistry
Osseointegration Without Surface Treatment
PEEK does not naturally bond to bone.
Surface treatment is required for implant body applications.
Lower Hardness vs Metallic Materials
PEEK is softer than metals.
It may scratch or wear faster in high-abrasion contacts.
Cost and Supply Considerations
Medical-grade PEEK costs more than common dental polymers.
Supply depends on qualified medical polymer producers.
Adhesion and Cementation Challenges
PEEK requires specific primers and surface treatments.
Standard dental cements may not bond effectively without preparation.
FAQs About PEEK Dental Material
Is PEEK FDA-approved for dental use?
Medical-grade PEEK is used in FDA-cleared and FDA-approved medical and dental devices when part of cleared systems. The FDA evaluates finished devices, not raw materials alone.
Can PEEK replace titanium implants?
PEEK cannot fully replace titanium for most implant bodies due to osseointegration limitations. It serves as a complementary material for abutments and frameworks.
Is PEEK better than zirconia for dental prosthetics?
PEEK offers better shock absorption and flexibility. Zirconia offers higher hardness and aesthetics. The choice depends on load, aesthetics, and design goals.
How long does PEEK last in dental applications?
When properly designed and processed, PEEK prosthetic components can last many years, comparable to other high-performance dental materials.
Making the Right Material Choice for Long-Term Clinical Success
PEEK dental material offers a unique combination of bone-like elasticity, radiolucency, biocompatibility, and lightweight performance. It does not replace titanium in all roles, but it clearly expands clinical and prosthetic design options. When used in abutments, frameworks, and metal-free prosthetics, PEEK supports both mechanical and aesthetic goals.
If you are evaluating medical-grade PEEK for dental applications, technical material selection y process validation are critical. Contact our team to discuss grades, machining guidance, bonding protocols, and OEM or dental lab supply options for predictable, compliant performance.






